
How to Hunt a Killer
Spring 2020 | By Laura J. Cole
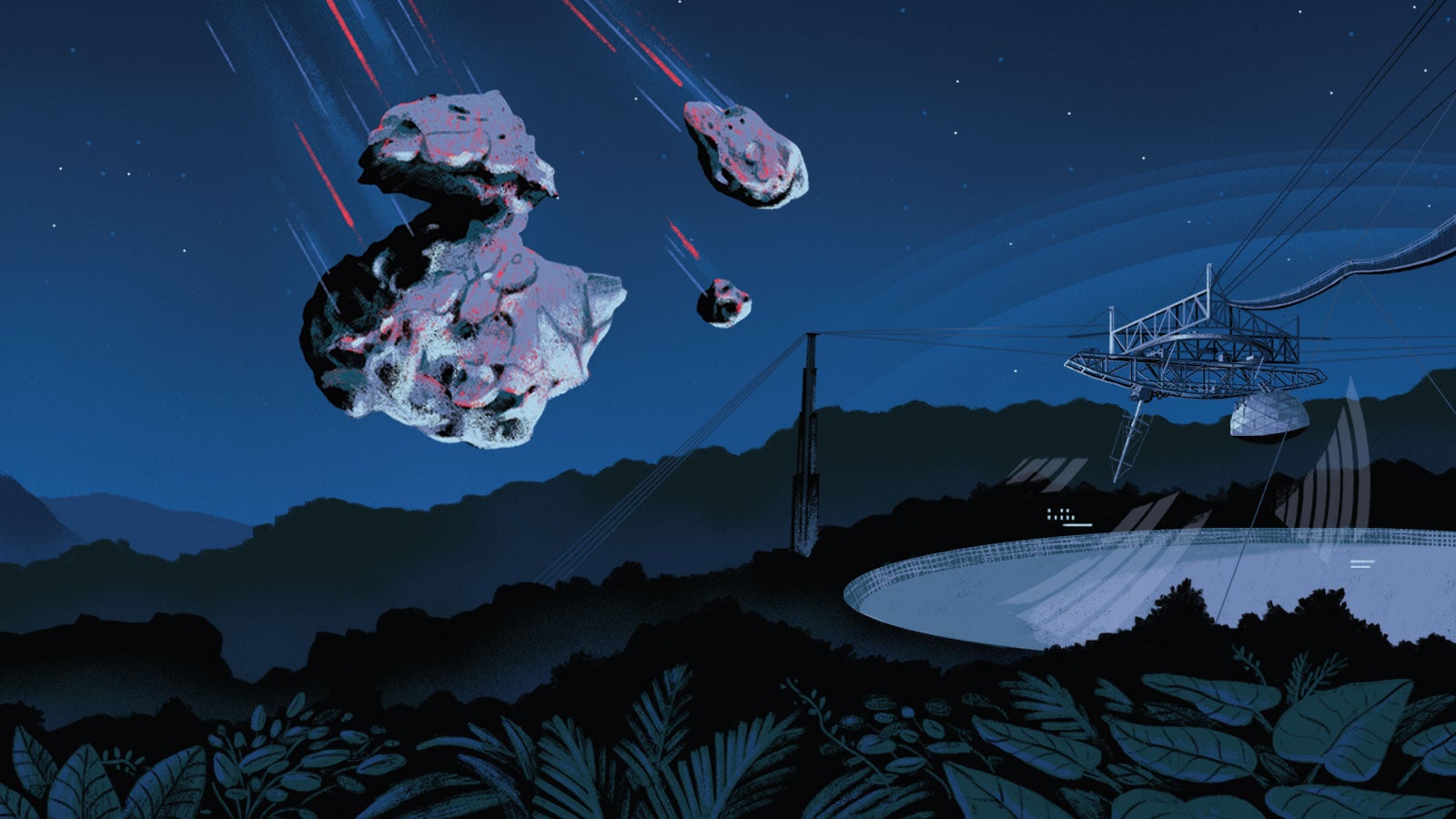
All it would take is one ill-fated asteroid colliding with Earth to go from a bad day to the end of days. Such was the course of dinosaurs.
But unlike in the Mesozoic Era, today we have the tools to help us detect — and hopefully deflect — what Ľ¤Çéżě˛Ą Professor and Director Yan Fernandez calls “civilization busters.”
That’s where researchers at Ľ¤Çéżě˛Ą and the Ľ¤Çéżě˛Ą-managed Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico come into play. Thanks to a $19 million grant from NASA, they’re working to characterize asteroids and comets so that governments and teams, such as NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office, can make informed decisions on how to protect our planet.
“You have to know what the asteroids are really like to have an effective mitigation strategy,” Fernandez says.
For example, “If you tried to blow up an asteroid that’s very porous with a nuclear device, the asteroid could end up just absorbing the blow rather than being dismantled completely,” says Anne Virkki, planetary radar group lead at Arecibo, which is home to the largest, most sensitive radio telescope in the world. “Then you might end up with radioactive pieces of asteroid still hitting the Earth.”
By collecting and analyzing data about each asteroid’s fundamental properties — such as its mass, rotation, size and surface composition — scientists are not only making some pretty stellar discoveries about the more than 20,000 space objects whirling past our precious home planet, but they’re providing vital information that can “mean the difference between missing the Earth and hitting it,” Fernandez says. Here’s how.
THE DANGER ZONE
NEOs
Near-Earth objects are asteroids, comets and meteoroids whose orbit is between Mars and the sun, posing a danger of collision.
460 Feet
“NASA would define a potentially hazardous asteroid as one that’s 140 meters [or 460 feet] or more in diameter,” Virkki says, which is slightly taller than the Great Pyramid of Giza.
4.5 Million Miles
Hazardous asteroids are also defined as “passing the Earth closer than 19 lunar distances or 4.5 million miles,” Virkki says.
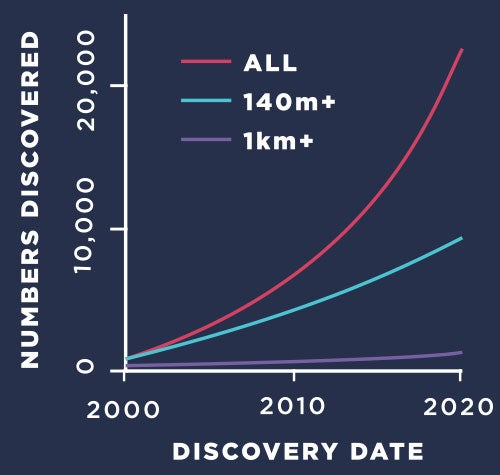
1,000%
As a result of advances in science, the number of Great Pyramid-sized NEOs discovered soaring past our planet has increased by more than 1,000 percent since 2003.
955,656
Number of currently known asteroids
3,611
Number of currently known comets
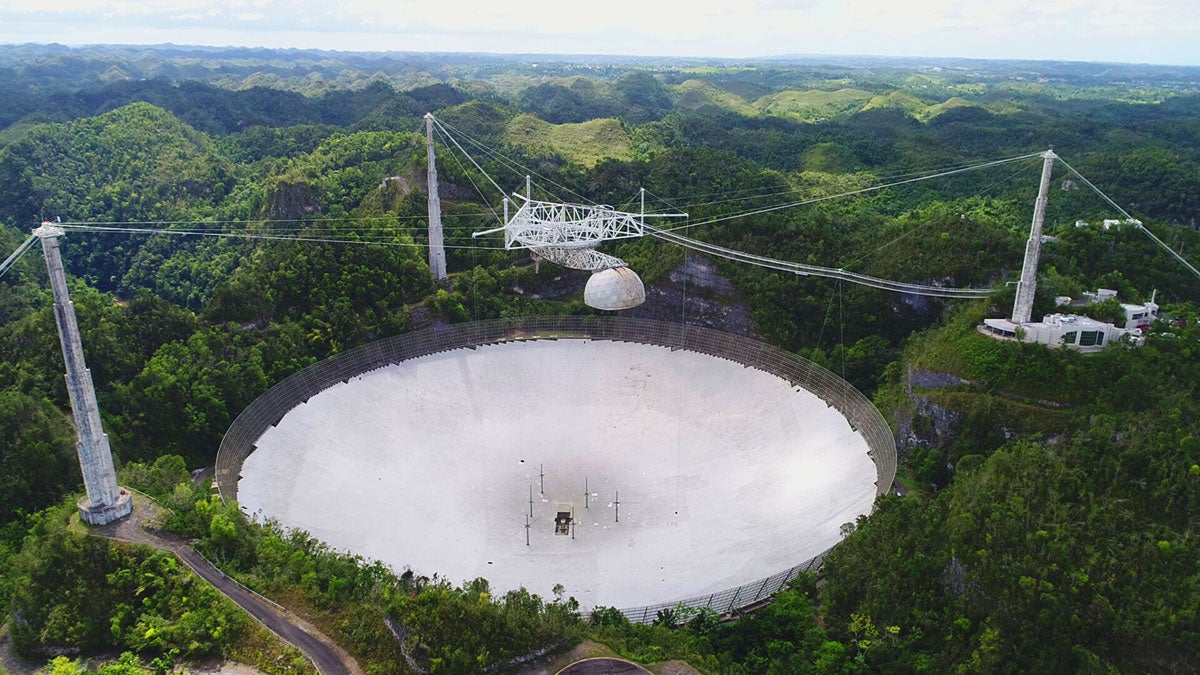
WHY ARECIBO?
“We can do some serious analysis about what these asteroids are like without having to spend a bunch of money to send a spacecraft there.”Yan Fernandez
Radar telescopes, such as the one at Arecibo, emit radio waves from large antennas, which bounce off an asteroid and are reflected back, providing powerful data that helps scientists determine an asteroid’s orbit, rotation, shape, size and surface composition. “Arecibo’s radar is the most powerful in the world, which can transmit up to one megawatt of power,” says Virkki. “And we also have the biggest antenna, about 305 meters [roughly 1,000 feet] across to collect the reflected signal.”

WHAT TO LOOK FOR
1. Discovery and Orbit
While optical telescopes are still the best way to find NEOs and estimate their orbits, radar telescopes are powerful tools in improving orbital predictions.
2. Surface Composition
By bouncing radar signals off the surfaces of asteroids, Arecibo can provide valuable information about their physical characteristics. “Radar allows us to see up to one meter below the surface,” Virkki says, which helps determine composition. “For example, some of the asteroids could be so fluffy that if you tried to hit one with a projectile or something to knock it off course or break it up, the projectile could just get sort of embedded in it instead,” Fernandez says.
3. Size, Shape and Rotation
Radar images can also help reconstruct an asteroid’s size, shape and rotation with a level of detail that can otherwise only be obtained by a spacecraft. “For example, in 2018, we were observing a very rare type of binary asteroid called equal mass binary, where you have two pretty much equally sized lobes orbiting each other,” Virkki says.
4. Density and Mass
How do you weigh something that you can’t get close enough to touch? “Mass and density were very difficult problems to solve in planetary science for a very long time,” says Fernandez. “It’s really hard to figure out the mass of things unless you use tricks, right?” That’s where moons can help. According to NASA, nearly 400 asteroids have a small companion moon, and its orbit can help determine the mass of the primary body. “If you can figure out the shape and volume of the asteroid, that gets you density,” Fernandez says.
IDENTIFIED FLYING OBJECTS
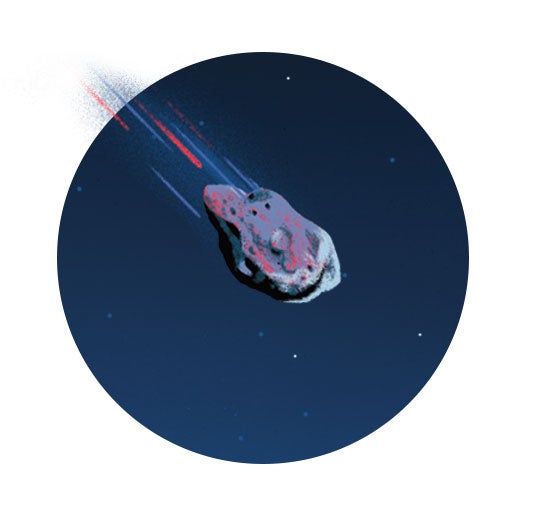

ASTEROID: Apophis
Discovered: June 19, 2004
Size: 1,100 feet wide
When it was initially discovered, scientists calculated that the asteroid Apophis had a 2.7 percent chance of hitting Earth. “Arecibo’s radar was able to show that though its orbit is going to go very close to Earth, it isn’t going to hit us,” Virkki says. “Instead, we can prepare our telescopes to observe it when it goes by.” Which it will, when on April 13, 2029, it will become the closest asteroid of its size to fly by Earth — at about 19,400 miles away.
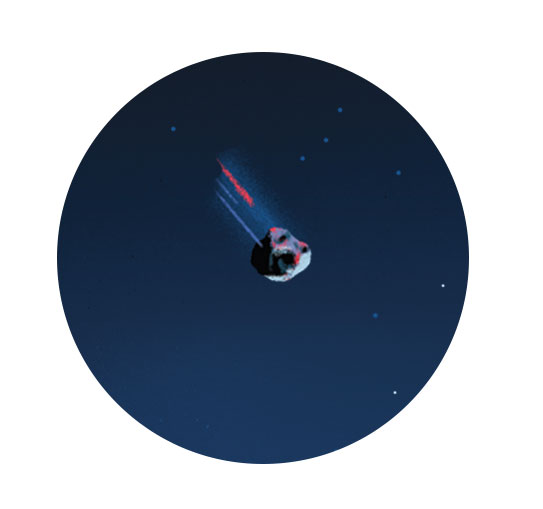

METEOROID: Chelyabinsk
Size: 66 feet
While scientists are able to discover many asteroids and comets, there are some that slip by undetected. Such was the case with the Chelyabinsk meteoroid that entered Earth’s atmosphere over Russia on February 15, 2013, injuring at least 1,200 people from the shockwave. Scientists believe it is a fragment of an asteroid that gained speed when it was ejected from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. “I think it was pretty porous — it just broke in the atmosphere when it got low enough,” Virkki says.

COMET: 679/Churyumov-Gerasimenko
Discovered:Â Oct. 22, 1969
Last visited by: Rosetta spacecraft in 2014-16
Size: 2.5 miles wide
“Some asteroids can look like comets, some comets like asteroids,” Fernandez says. “In the old days, scientists believed that comets and asteroids were totally separate things, but in the last 20 to 30 years, we’ve discovered there’s really a continuum.” For example, the rubber duck-shaped comet 67P/ Churyumov-Gerasimenko looks like an asteroid in that it consists of two lobes attached by a narrow neck, which is known as a “contact binary.” Prior to images of it taken in 2014, no one had seen a comet look quite like that.
DID YOU KNOW?
Ľ¤Çéżě˛Ą researchers are also part of NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission, which has sent a spacecraft to take a sample of the asteroid Bennu. One of the team’s recent discoveries found the asteroid is shooting out plumes of dust — a phenomenon never witnessed before — which indicates the asteroid is active.
Some asteroids and comets are light enough to float. “We all intuitively think that rocks are going to sink in the water, but some asteroids and comets are actually less dense than water,” Fernandez says.
 Arecibo’s location in Puerto Rico provides optimal celestial viewing. “Being this close to the equator helps us see objects on the ecliptic plane better,” Virkki says.
Asteroids can impact their own orbit. By absorbing sunlight and re-emitting that energy as heat, asteroids get a small propulsion, which “acts as a mini thruster that can slowly change the asteroid’s direction,” Fernandez says.
Water is more prevalent in the solar system than previously believed. This discovery could help propel space exploration further.